My SpringCloudLearn
什么是微服务
在我的理解上微服务就是前后端分离的变种,只不过是拆分的更加彻底一些,比如用户的查询,商品的查询,等等每一个都作为一个单独的服务剥离出来而已.
优点
每个微服务都是一个独立的Spring Cloud程序,他们可以整体写作变成一个大的Spring Cloud程序,优点是不会对其他的Spring Cloud影响,且可以使用不同的语言进行开发,还可以根据服务的请求量来配置不同的服务器,由于每个服务都是独立开发,项目的开发也比较方便,减少代码冲突,代码重复,逻辑处理也会更加清晰,让后续的维护与扩产更加容易.
缺点
- 增加了系统维护,部署的难度,导致一些功能模块或代码无法复用.
- 随着系统规模日渐增长,微服务在一定程度上也会导致系统扁的越来越复杂,增加了集成测试的复杂度.
- 随着微服务的增多,数据的一致性问题,服务之间的通信成本等都凸显了出来.
Spring Cloud是什么
Spring Cloud是一个基于Spring Boot框架构建微服务架构,为开发者提供了一系列的构建分布式系统的工具集,比如配置管理,服务发现,断路器,智能路由,微代理,控制总线,全局锁,决策竞选,分布式会话和集群状态管理等.
Spring Cloud的整体架构
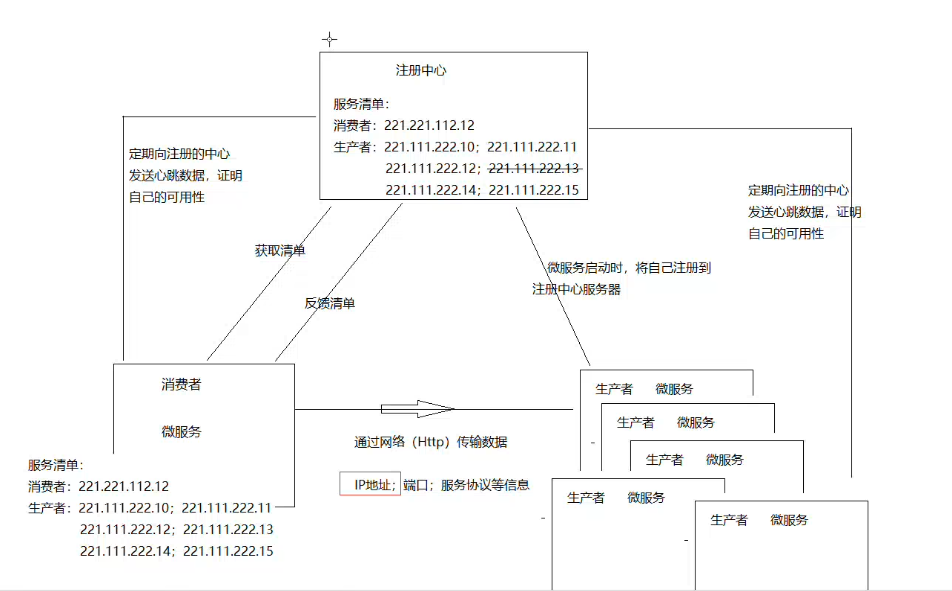
Spring Cloud快速入门
搭建一个基础的
springboot环境新建一个生产者
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class HelloController {
public String hello() {
return "hello Spring Cloud";
}
}新建一个消费者
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class TestController {
public String test(){
return "consumer";
}
}修改消费者端口
1
server.port=8091
使用
RestTemplate进行程序间的相互通讯在主类中添加方法,或新建类添加注解
@Configuration1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9/*
相当于bean标签的作用
<bean class="RestTemplate" id="restTemplate" />
RestTemplate对象,用于在进程之间发送请求获取数据
*/
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}使用
RestTemplate向生产者hello发送请求,并得到应答结果1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public class TestController {
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
public String test() {
/*
* restTemplate 用于在不同服务之间请求数据
* getForEntity方法,使用get方式请求数据,返回结果为远端服务的反馈信息+其他信息(请求返回的状态码等)
* 参数1: 请求服务的地址
* 参数2: 应答的数据类型
* getBody: 用于获取应答数据中远端服务器返回的内容
*
*/
//String result = restTemplate.getForEntity("http://localhost:8080/hello", String.class).getBody();
//Object[] parmas = {1, "test"};
//restTemplate.getForEntity("http://SPRINGCLOUD01/hello{1}/{2}", String.class, parmas);
//Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//map.put("id",1);
//map.put("name","test");
//restTemplate.getForEntity("http://SPRINGCLOUD01/hello{id}/{name}", String.class, map);
String result = restTemplate.getForEntity("http://SPRINGCLOUD01/hello", String.class).getBody();
return "consumer " + result;
}
}getForEntity通过拼接占位符的方式来传递url
注册中心Eureka
注册中心就是将访问所在的主机,端口,版本号,通信协议等信息登记到注册中心,好让注册中心做服务的统一调度与均衡负载.
Eureka是什么
Eureak是一个服务治理组件,它主要包括服务注册和服务发现,进行中间层服务器的负载均衡和故障转移,有了Eureak注册中心开发者可以通过Eureka Server来监控系统中各个微服务是否正常运行.
搭建与配置Eureka
新建项目
- 新建
Spring Boot项目时勾选Spring Cloud Discovery→Eureka Server - 修改
Spring Boot版本为2.3.10.RELEASE - 修改
Spring Cloud版本为Hoxton.SR11
简单配置
在
主类中添加注解@EnableEurekaServer1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
//声明当前程序是eureka注册中心
public class SpringCloudEureakApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudEureakApplication.class, args);
}
}配置
eureak基础内容1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10#当前微服务端口号
server.port=9100
#声明eureka服务域名
eureka.instance.hostname=localhost
#不需要将当前服务器注册到eureka(自己)
eureka.client.fetch-registry=false
#不需要去获取服务清单
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=false
#提供给eureka客户端的注册地址
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka
注册微服务
生产者
在主类中添加
@EnableEurekaClient1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
//声明当前项目为eureka客户端
public class SpringcloudApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringcloudApplication.class, args);
}
}配置
eureka基础内容1
2
3
4
5server.port=8081
#应用程序名字
spring.application.name=springcloud01
#eureka注册中心地址
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:9100/eureka
消费者
在主类中添加
@EnableEurekaClient在
restTemplate方法上添加@LoadBalanced1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class SpringcloudconsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringcloudconsumerApplication.class, args);
}
//使用 ribbon 负载均衡
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}配置
eureka基础内容1
2
3
4
5server.port=8082
#应用程序名称
spring.application.name=consumer
#eureka注册中心地址
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:9100/eureka修改
消费者的test方法restTemplate请求地址,即可实现负载均衡1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public class TestController {
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
public String test() {
/*
* restTemplate 用于在不同服务之间请求数据
* getForEntity方法,使用get方式请求数据,返回结果为远端服务的反馈信息+其他信息(请求返回的状态码等)
* 参数1: 请求服务的地址
* 参数2: 应答的数据类型
* getBody: 用于获取应答数据中远端服务器返回的内容
*
*/
//String result = restTemplate.getForEntity("http://localhost:8080/hello", String.class).getBody();
String result = restTemplate.getForEntity("http://SPRINGCLOUD01/hello", String.class).getBody();
return "consumer " + result;
}
}
高可用集群
- 搭建两个
eureka注册中心,并且注册地址指向对方即可 - 微服务
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone注册中心可添加多个,使用,分割eureka会自动寻找可用的注册中心进行注册1
2#eureka注册中心地址
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://eureka9100:9100/eureka,http://eureka9200:9200/eureka
Eureka自我保护机制

在没有Eureka自我保护的情况下,如果Eureka Server在一定时间内没有接收到某个微服务的心跳,Eureka Server将会注销该实例但是在发生网络分区故障时,那么微服务与Eureka Server之间将无法正常通信,一上行为就可能变的非常危险了
- 因为微服务本身其实是正常的,此时不应该注销这个微服务,如果没有自我保护机制,那么Eureka Server就会将次服务注销掉
Eureka通过
自我保护模式来解决这个问题 , 当Eureka Server节点在短时间内丢失过多客户端时(可能发生了网络分故障),那么就会把这个微服务节点进行保护- 一旦进入自我保护模式, Eureka Server就会保护服务注册表中的信息,不删除服务注册表中的数据,也就是说不会注销任何微服务,当网络故障恢复后,Eureka Server节点会自动退出自我保护模式
- 但是Eureka自我保护模式,如果在保护器内某个服务提供者刚好非正常下线了,此时服务消费者,就会拿到一个无效的服务实力,此时会调用失败,对于这个问题需要消费者端具有一定的容错机制
关闭自我保护模式
1 | eureka.server.enable-self-preservation=false |
发送心跳
1 | #每间隔2s,向服务端发送一次心跳,证明自己"活着" |
服务熔断Hystrix
在微服务架构中,将单体应用拆分成多个服务单元,各个服务单元之前通过注册中心彼此发现和消费对方提供的服务,那么当某个服务的响应太慢或故障,则会造成调用者延迟或调用失败,当大量请求到达则会造成请求的堆积,导致调用者的线程挂起,从而引发调用者也无法响应,调用者也发送故障,为了解决问题,微服务架构中引入了一种叫熔断器的服务保护机制.
熔断器也有叫断路器,微服务架构中熔断器就是当调用方没有响应,调用方直接返回一个错误响应即可,而不是长时间的等待,这样避免调用时因为等待而线程一直得不到释放,避免故障在分布式系统间蔓延.
这种状态类似于保险丝,当电流过载后保险丝会被烧断,从而保护电路.
Feign
添加
Feign客户端依赖 或 新建项目勾选Spring Cloud Routing→OpenFeign1
2
3
4<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>主类中添加
@EnableFeignClients注解,开启Feign创建
接口1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13/*
* 用这个接口访问 SPRINGCLOUD01 微服务
*/
public interface TestFeign {
/*
* 要访问的微服务资源路径
*/
String test();
}创建
controller1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class TestController {
private TestFeign testFeign;
public String test() {
String ret = testFeign.test();
return "feign client " + ret;
}
}
Hystrix快速入门
添加依赖
1
2
3
4<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>添加配置
application.properties1
2#开启feign的熔断降级功能
feign.hystrix.enabled=true新建类用于处理异常
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class TestFallBack implements TestFeign {
public String test() {
return "feign 异常";
}
}为
feign添加fallback- fallback = TestFallBack.class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13/*
* 用这个接口访问 SPRINGCLOUD01 微服务
*/
public interface TestFeign {
/*
* 要访问的微服务资源路径
*/
String test();
}
Fallback Factory
相比于
FallBack我们无法得知错误信息FallbackFactory可以有效的获取错误代码与时间等1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class TestFallBackFactory implements FallbackFactory<TestFeign> {
public TestFeign create(Throwable throwable) {
return new TestFeign() {
public String test() {
return throwable.getMessage();
}
};
}
}返回结果
feign client [500] during [GET] to [http://SPRINGCLOUD01/hello] [TestFeign#test()]: [{“timestamp”:”2022-01-11T07:21:36.023+00:00”,”status”:500,”error”:”Internal Server Error”,”message”:””,”path”:”/hello”}]
服务的降级
服务降级是指,某个服务熔断后,服务端提供的服务将不再被调用,此时由客户端自己准备的一个本地Fallback回调,返回一个默认值代表服务端返回,虽然客户端不会得到正确的数据,但是
Hystrix仪表盘
添加依赖
1
2
3
4<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
</dependency>在主类添加注解
@EnableHystrixDashboard向需要被监控的微服务添加依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>添加配置
1
2#设置解控端点可以被访问
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*访问
http://localhost:8091/actuator/hystrix.stream查看是否生成了页面将步骤
5的url填入至http://localhost:3721/hystrix即可查看
API网关Zuul
在微服务中,一个独立的系统被拆分成了很多个独立服务,为了确保安全,权限管理也是一个不可回避的问题,为了解决上述问题微服务架构中提出了API网关的概念,他就想一个安监站一样,所有外部的请求都需要经过他的调度与过滤,然后API网关来实现请求路由,均衡负载,权限验证等功能
- 我觉得吧这东西类似于Filter,但是他负责的东西更多一些
使用Zuul构建网关
添加依赖
1
2
3
4<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-zuul</artifactId>
</dependency>主类添加注解
@EnableZuulProxy添加配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18#请求路径
#http://localhost:8888/springcloud/hello = http://SPRINGCLOUD01/hello
#zuul.routes.springcloud.path=/springcloud/**
##转发到 SPRINGCLOUD01
#zuul.routes.springcloud.service-id=SPRINGCLOUD01
#简易方式 zuul.routes.服务名.path
zuul.routes.SPRINGCLOUD01.path=/springcloud/**
#忽略掉某一些接口路径
#zuul.ignored-patterns=/**/hello/**
#多加一级路径 (http://localhost:8888/springcloud/api/hello)
#zuul.prefix=/api
#转发zuul网关自身路径
zuul.routes.zuulocal.path=/zuullocal/**
zuul.routes.zuullocal.url=forward:/api/local
| 通配符 | 含义 | 用法举例 | 匹配说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ? | 匹配单个字符 | /api/hello/? | /api/hello/a /api/hello/b /api/hello/c等 |
| * | 匹配任意数量字符 | /api/hello/* | /api/hello/abcdefg |
| ** | 匹配任意数量字符 | /api/hello/** | /api/hello/abcdefg /api/hello/a/b/c/d/e/f/g |
Zuul过滤器
- 新建类 继承
ZuulFilter
1 |
|
Zuul异常处理
添加配置
1
2#开启拦截器异常
zuul.SendErrorFilter.error.disable=true新建异常类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
public class MyErrorFilter extends ZuulFilter {
public String filterType() {
return "error";
}
public int filterOrder() {
return 1;
}
public boolean shouldFilter() {
return true;
}
public Object run() throws ZuulException {
try {
System.out.println("捕获到过滤器异常");
RequestContext context = RequestContext.getCurrentContext();
ZuulException zuulException = (ZuulException) context.getThrowable();
System.out.println(zuulException);
HttpServletResponse response = context.getResponse();
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.setStatus(zuulException.nStatusCode);
PrintWriter writer = null;
writer = response.getWriter();
writer.write("{'code':" + zuulException.nStatusCode + ",msg:'" + zuulException.getMessage() + "'}");
} catch (IOException e) {
ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(e);
}
return null;
}
}
ErrorController异常处理
1 |
|




